Software
Equipment that is increasingly multi-functional and multi-energy, together with increasingly complex control and regulation systems, make it difficult to design or evaluate performance through experimentation alone. CETIAT uses the latest numerical simulation tools to cover all these questions.
NUMERICAL SIMULATION
The use of numerical models, whether coupled with physical tests or not, accelerates development while reducing costs for a range of activities:- designing or pre-specifying new solutions,
- diagnostics and improved operation of equipment, components, systems etc.
- predicting a product's performance at all stages of its development.
OUR MULTI-PHYSICAL APPROACH
CETIAT's experts rely on powerful dedicated computer tools and perform:- CFD numerical simulations of fluid flows (gases, liquids), heat transfers (conductive, convective, radiative) and particle trajectories (droplets, dust),
- EM simulations of electrostatic and electromagnetic fields in furnaces and applicators using radiant energy,
- TSS simulations of transient multi-module systems of interconnected dynamic components with their own connection and regulation systems (HVAC components: exchangers, tanks, etc.).
EXAMPLE APPLICATIONS
Unstable CFD simulation of flows and temperature fields in a hot water tank
The objective is to visualise heating - the temperature rise in relation to time - and therefore to anticipate the effects of technical design choices.
Temperature rise in a hot water tank
CFD simulation of particle trajectories in a dust collection system
The objective is to verify the spectral efficiency of the system, i.e. its ability to capture the particles according to their diameter. It is also possible to visualise the distribution of the particles collected in the hopper according to their size.
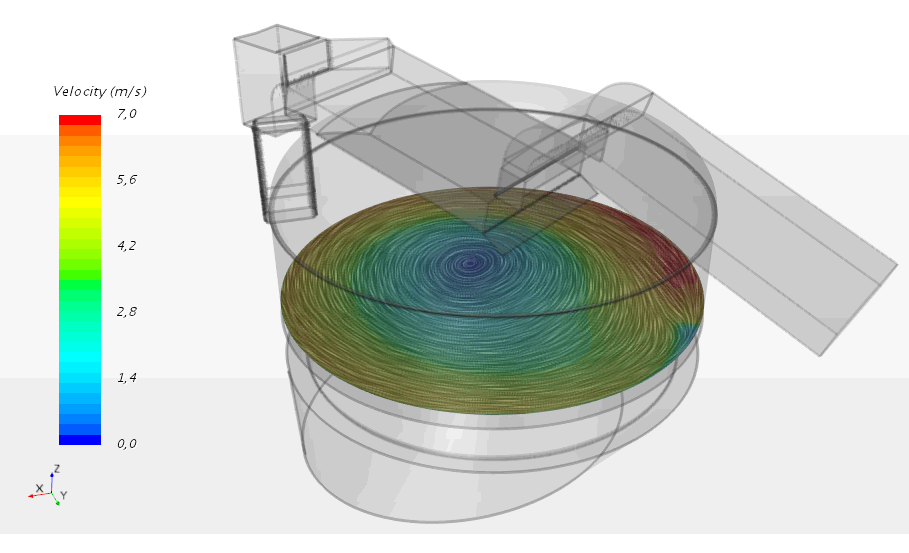
Centrifugation of flow in a dust collection system
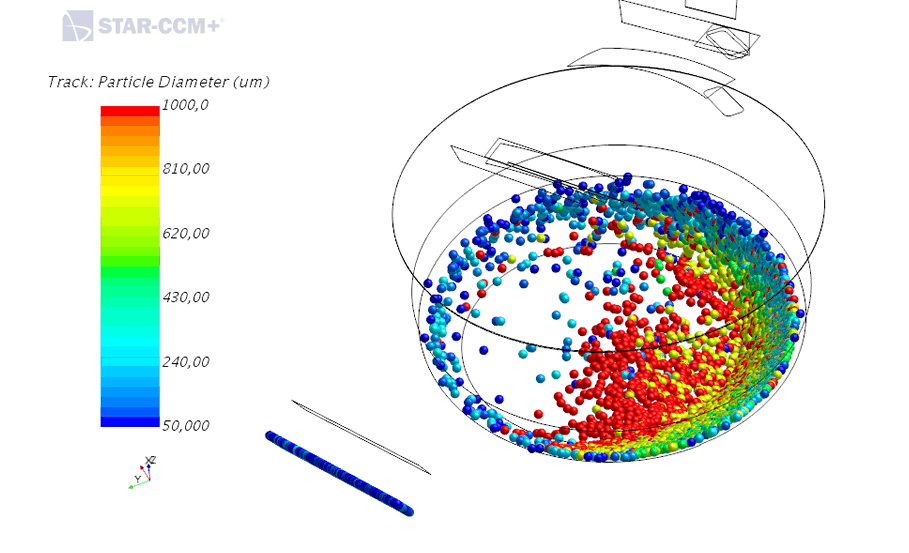
Particle trajectory in a dust collection system
EM simulation of electric fields in a microwave oven
The objective is to validate the design by visualising the fields in space in order to verify their homogeneity, and to detect possible problem areas.
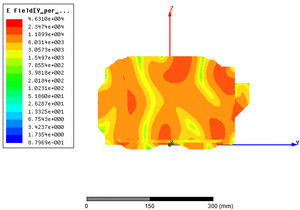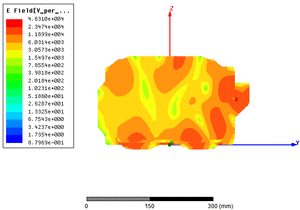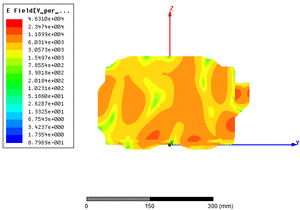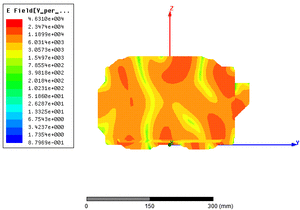
Electric field distribution in a microwave oven
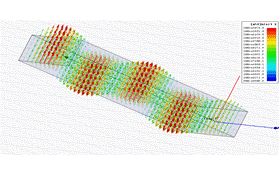
Wave propagation in a waveguide
TSS simulation of an HVAC component
The objective is to predict the time-dependent operation of an HVAC system and its components by testing different control solutions, different choices of components or connection configurations etc.
1D simulation of a dual-function boiler
SOFTWARE USED
- CFD (Computational Fluid Dynamics): STAR-CCM+ (Siemens), FLUENT (Ansys)
- CAD (Computer Aided Design): ANSA (Beta-cae)
- EM (Electromagnetic Modelling): HFSS (Ansys)
- TSS (Transient System Simulations): TRNSYS
- Multiple specific in-house tools
COMPUTING CAPABILITIES
- CentOS Linux supercomputer
- 192 Intel Xeon 2.6 processors (12*16)
- 56 Gb/s FDR InfiniBand
- 768 GB RAM

